Studying rivers from worlds away
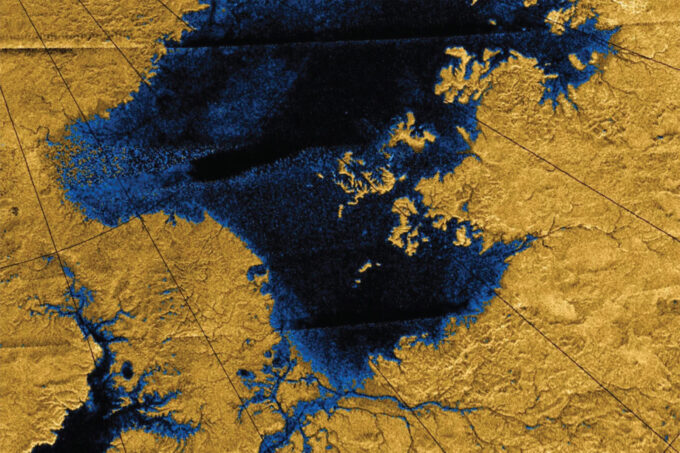
Images from the Cassini mission show river networks draining into lakes in Titan’s north polar region. Image credit: NASA/JPL/USGS
Rivers have flowed on two other worlds in the solar system besides Earth: Mars, where dry tracks and craters are all that’s left of ancient rivers and lakes, and Titan, Saturn’s largest moon, where rivers of liquid methane still flow today.
A new technique developed by MIT geologists allows scientists to see how intensely rivers used to flow on Mars, and how they currently flow on Titan. The method uses satellite observations to estimate the rate at which rivers move fluid and sediment downstream.
Applying their new technique, the MIT team calculated how fast and deep rivers were in certain regions on Mars more than 1 billion years ago. They also made similar estimates for currently active rivers on Titan, even though the moon’s thick atmosphere and distance from Earth make it harder to explore, with far fewer available images of its surface than those of Mars.
“What’s exciting about Titan is that it’s active. With this technique, we have a method to make real predictions for a place where we won’t get more data for a long time,” says Taylor Perron, the Cecil and Ida Green Professor in MIT’s Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences (EAPS). “And on Mars, it gives us a time machine, to take the rivers that are dead now and get a sense of what they were like when they were actively flowing.”
Perron and his colleagues have published their results today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Perron’s MIT co-authors are first author Samuel Birch, Paul Corlies, and Jason Soderblom, with Rose Palermo and Andrew Ashton of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), Gary Parker of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, and collaborators from the University of California at Los Angeles, Yale University, and Cornell University.
River math
The team’s study grew out of Perron and Birch’s puzzlement over Titan’s rivers. The images taken by NASA’s Cassini spacecraft have shown a curious lack of fan-shaped deltas at the mouths of most of the moon’s rivers, contrary to many rivers on Earth. Could it be that Titan’s rivers don’t carry enough flow or sediment to build deltas?
The group built on the work of co-author Gary Parker, who in the 2000s developed a series of mathematical equations to describe river flow on Earth. Parker had studied measurements of rivers taken directly in the field by others. From these data, he found there were certain universal relationships between a river’s physical dimensions — its width, depth, and slope — and the rate at which it flowed. He drew up equations to describe these relationships mathematically, accounting for other variables such as the gravitational field acting on the river, and the size and density of the sediment being pushed along a river’s bed.
“This means that rivers with different gravity and materials should follow similar relationships,” Perron says. “That opened up a possibility to apply this to other planets too.”
Getting a glimpse
On Earth, geologists can make field measurements of a river’s width, slope, and average sediment size, all of which can be fed into Parker’s equations to accurately predict a river’s flow rate, or how much water and sediment it can move downstream. But for rivers on other planets, measurements are more limited, and largely based on images and elevation measurements collected by remote satellites. For Mars, multiple orbiters have taken high-resolution images of the planet. For Titan, views are few and far between.
Birch realized that any estimate of river flow on Mars or Titan would have to be based on the few characteristics that can be measured from remote images and topography — namely, a river’s width and slope. With some algebraic tinkering, he adapted Parker’s equations to work only with width and slope inputs. He then assembled data from 491 rivers on Earth, tested the modified equations on these rivers, and found that the predictions based solely on each river’s width and slope were accurate.
Then, he applied the equations to Mars, and specifically, to the ancient rivers leading into Gale and Jezero Craters, both of which are thought to have been water-filled lakes billions of years ago. To predict the flow rate of each river, he plugged into the equations Mars’ gravity, and estimates of each river’s width and slope, based on images and elevation measurements taken by orbiting satellites.
From their predictions of flow rate, the team found that rivers likely flowed for at least 100,000 years at Gale Crater and at least 1 million years at Jezero Crater — long enough to have possibly supported life. They were also able to compare their predictions of the average size of sediment on each river’s bed with actual field measurements of Martian grains near each river, taken by NASA’s Curiosity and Perseverance rovers. These few field measurements allowed the team to check that their equations, applied on Mars, were accurate.
The team then took their approach to Titan. They zeroed in on two locations where river slopes can be measured, including a river that flows into a lake the size of Lake Ontario. This river appears to form a delta as it feeds into the lake. However, the delta is one of only a few thought to exist on the moon — nearly every viewable river flowing into a lake mysteriously lacks a delta. The team also applied their method to one of these other delta-less rivers.
They calculated both rivers’ flow and found that they may be comparable to some of the biggest rivers on Earth, with deltas estimated to have a flow rate as large as the Mississippi. Both rivers should move enough sediment to build up deltas. Yet, most rivers on Titan lack the fan-shaped deposits. Something else must be at work to explain this lack of river deposits.
In another finding, the team calculated that rivers on Titan should be wider and have a gentler slope than rivers carrying the same flow on Earth or Mars. “Titan is the most Earth-like place,” Birch says. ”We’ve only gotten a glimpse of it. There’s so much more that we know is down there, and this remote technique is pushing us a little closer.”
This research was supported, in part, by NASA and the Heising-Simons Foundation.